Clinical Research
(CR-055) Enhancing Home Health Performance: Clinical and Operational Impacts of Digital Wound Care Technology at Home Health
Friday, May 2, 2025
7:45 PM - 8:45 PM East Coast USA Time
Robert D. J. Fraser, MN RN NSWOC WOCC(C) – Swift Medical Inc.; Tameka McCabe, BSN, RN, WCC; James Grey, BA,RN; Amy Cassata, BSN, RN, WCC
Introduction: Wounds significantly increase the risk of hospitalization in home health (HH) settings by up to 52%. 1 They also consume a notable portion of HH budgets with the frequent nursing visits for wound assessment and care.2 To address these challenges, a U.S.-based HH enterprise adopted a Digital Wound Care Solution (DWCS) to enhance wound management and operational efficiency. This benefits evaluation study examines the impact of integrating the DWCS into practice, focusing on clinical and operational indicators and associated cost savings.
Methods: Data were gathered from the DWCS and EMR databases, encompassing pre- and post-adoption phases of DWCS in 2022 and 2023. The analysis included wound data from 16,276 patients in 2023 and 19,252 patients in 2022, covering an 8-month period (March–October) across 11 branches. The key performance indicators (KPIs) included skilled nursing (SN) visits per episode (VPE), time to complete SN visits, wound healing duration, hospitalization rates, adherence to best practices, and staff optimization.
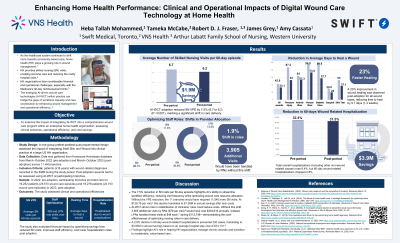
Results: The adoption of the DWCS led to notable clinical and operational improvements. SN VPE decreased by 7.5%, resulting in an estimated annual savings of $1.3 million. Wound healing time improved by 22.7%, with an average reduction of 9.7 days in healing time across wound types. Hospitalization rates attributable to wound complications decreased by 2.8%, preventing 200 hospitalizations with a projected annual cost savings of $3.4 million to the health system. A 1.9% shift in staff roles increased the utilization of Licensed Practical Nurses without compromising care quality, saving $112,748 annually. Adherence to best practices improved by 7%, with increased wound imaging frequency during assessments. Additionally, staff efficiency improved by 2.1%, saving 114 staff days annually and yielding potential savings of $200,000.
Discussion: The implementation of the DWCS significantly enhances clinical outcomes and operational efficiencies, resulting in substantial cost savings, aligning with value-based care objectives, which offers scalable benefits for HH enterprises.
Methods: Data were gathered from the DWCS and EMR databases, encompassing pre- and post-adoption phases of DWCS in 2022 and 2023. The analysis included wound data from 16,276 patients in 2023 and 19,252 patients in 2022, covering an 8-month period (March–October) across 11 branches. The key performance indicators (KPIs) included skilled nursing (SN) visits per episode (VPE), time to complete SN visits, wound healing duration, hospitalization rates, adherence to best practices, and staff optimization.
Results: The adoption of the DWCS led to notable clinical and operational improvements. SN VPE decreased by 7.5%, resulting in an estimated annual savings of $1.3 million. Wound healing time improved by 22.7%, with an average reduction of 9.7 days in healing time across wound types. Hospitalization rates attributable to wound complications decreased by 2.8%, preventing 200 hospitalizations with a projected annual cost savings of $3.4 million to the health system. A 1.9% shift in staff roles increased the utilization of Licensed Practical Nurses without compromising care quality, saving $112,748 annually. Adherence to best practices improved by 7%, with increased wound imaging frequency during assessments. Additionally, staff efficiency improved by 2.1%, saving 114 staff days annually and yielding potential savings of $200,000.
Discussion: The implementation of the DWCS significantly enhances clinical outcomes and operational efficiencies, resulting in substantial cost savings, aligning with value-based care objectives, which offers scalable benefits for HH enterprises.

.jpg)