Case Series/Study
(CS-085) A Novel Application of KCI Prevena Adaptiform for Patients at High Risk of Poor Amputation Healing
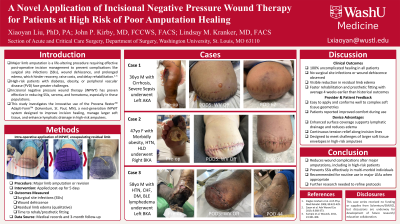
Major limb amputation is a life-altering procedure affecting approximately 2 million Americans, a number projected to double by 2050. Effective post-operative incision management is crucial to reduce complications such as surgical site infections (SSIs), wound dehiscence, and prolonged edema, which delay recovery, increase healthcare costs, and impair rehabilitation. These challenges are further compounded in high-risk patients with comorbidities like diabetes, obesity, and peripheral arterial disease. Incisional negative pressure wound therapy (iNPWT) has demonstrated efficacy in reducing SSIs, seroma, and hematoma formation, particularly in high-risk populations. This study explores the novel application of the Prevena Adaptiform (KCI, 3M Company), a second-generation iNPWT system designed to optimize incision healing, manage larger soft tissue envelopes, and enhance lymphatic drainage in this challenging population.
Methods:
This retrospective case series evaluated four high-risk patients undergoing major limb amputation or revision who were treated with the Prevena Adaptiform. The system was applied immediately post-operatively and maintained for five days per manufacturer guidelines. Patient selection criteria included the presence of significant comorbidities, such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. Outcomes assessed included rates of SSIs, incidence of wound dehiscence, reduction in residual limb edema (measured qualitatively), and time to rehabilitation or prosthetic fitting. Data were collected from medical records and three-month follow-up visits.
Results:
The Prevena Adaptiform system demonstrated 100% uncomplicated healing in all cases, with no SSIs or dehiscence observed. Residual limb edema was visibly reduced in all patients, contributing to faster rehabilitation timelines and earlier prosthetic fitting by an average of two weeks compared to historical outcomes. Ease of application and the ability to conform to complex soft tissue geometries were noted as key benefits by providers, while patients reported improved comfort during use. This case series highlights the potential of the Prevena Adaptiform system to improve post-operative outcomes in high-risk amputation patients, representing a promising advancement in wound care management.
Discussion: The Prevena Adaptiform system builds on traditional iNPWT by addressing the unique challenges of larger soft tissue envelopes in high-risk amputees. Its enhanced surface coverage promotes lymphatic drainage, reduces soft tissue edema, and provides continuous tension relief along incision lines. These features not only reduce complications but also support faster recovery and improved quality of life. Future studies comparing this system to traditional iNPWT and standard care are warranted to establish best practices and cost-effectiveness.

.jpg)