Case Series/Study
(CS-087) Adipose Injectable Filler with Use of Meshed Dermal Matrix and Porcine Urinary Bladder Matrix for the Management of a Complex Achilles Wound
Friday, May 2, 2025
7:45 PM - 8:45 PM East Coast USA Time
Orlexia Thomas, DPM; Mariam Kamil, BS; Lady DeJesus, DPM, FACFAS, FACPM, CWSP
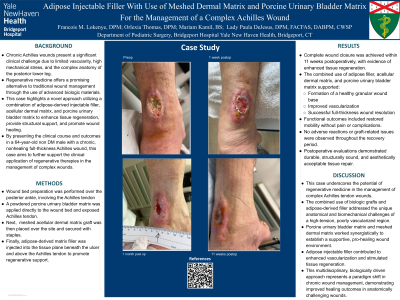
Introduction: The purpose of this case study is to demonstrate the efficacy of combining adipose injectable filler, dermal matrix, and porcine urinary bladder matrix in the management of a complex achilles wound. This novel approach seeks to enhance tissue regeneration, provide structural support, and promote wound healing in a challenging anatomical location. By documenting the clinical outcomes and procedural details, this case regarding a 64 year old male with a non-healing full thickness achilles wound, aims to contribute to the growing body of evidence supporting regenerative medicine techniques for chronic wound care.
Methods: The wound to the posterior ankle about the achilles tendon was debrided to a granular base. A powdered porcine urinary bladder matrix was applied to the wound bed and achilles tendon, followed by placement of a meshed dermal matrix graft secured with staples. Next, adipose matrix filler was injected into the tissue plane beneath the ulceration site and above the achilles tendon to support regeneration. This demonstrates a multidisciplinary approach with a combination of sharp wide excisional debridement, biologic grafts, and adipose filler for effective wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Results: There was complete closure of the wound with improved tissue regeneration 11 weeks after surgery. The combined use of adipose filler, dermal matrix, and porcine urinary bladder matrix promoted a healthy granular base, enhanced vascularization, and assisted in complete wound closure. Functional outcomes included restored mobility without pain or complications. There were no adverse reactions, and post-procedure evaluations confirmed durable and aesthetically acceptable tissue repair.
Discussion: This case highlights the transformative potential of regenerative medicine in managing complex Achilles wounds. By combining the structural support of biologic grafts with the regenerative capabilities of adipose fillers, this approach addressed the anatomical and biomechanical challenges of a high-tension area and hard to heal areas due to poor vascularity. The porcine urinary bladder matrix and meshed dermal matrix synergistically created an optimal healing environment, while the adipose injectable filler improved vascularity and stimulated regeneration. This innovative strategy exemplifies a paradigm shift in chronic wound care, offering superior outcomes.
Methods: The wound to the posterior ankle about the achilles tendon was debrided to a granular base. A powdered porcine urinary bladder matrix was applied to the wound bed and achilles tendon, followed by placement of a meshed dermal matrix graft secured with staples. Next, adipose matrix filler was injected into the tissue plane beneath the ulceration site and above the achilles tendon to support regeneration. This demonstrates a multidisciplinary approach with a combination of sharp wide excisional debridement, biologic grafts, and adipose filler for effective wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Results: There was complete closure of the wound with improved tissue regeneration 11 weeks after surgery. The combined use of adipose filler, dermal matrix, and porcine urinary bladder matrix promoted a healthy granular base, enhanced vascularization, and assisted in complete wound closure. Functional outcomes included restored mobility without pain or complications. There were no adverse reactions, and post-procedure evaluations confirmed durable and aesthetically acceptable tissue repair.
Discussion: This case highlights the transformative potential of regenerative medicine in managing complex Achilles wounds. By combining the structural support of biologic grafts with the regenerative capabilities of adipose fillers, this approach addressed the anatomical and biomechanical challenges of a high-tension area and hard to heal areas due to poor vascularity. The porcine urinary bladder matrix and meshed dermal matrix synergistically created an optimal healing environment, while the adipose injectable filler improved vascularity and stimulated regeneration. This innovative strategy exemplifies a paradigm shift in chronic wound care, offering superior outcomes.

.jpg)