Evidence-Based Practice
(EBP-014) A Multi-national Survey of Healthcare Professionals’ Experiences of Gelling Fiber Wound Dressings for Different Wound Types
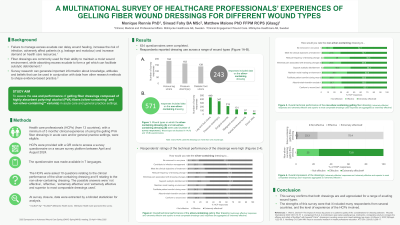
Gelling fiber dressings are widely used to absorb and retain excess exudate. Real-world usage characteristics, product performance, and strengths/weaknesses (e.g., one piece removal) vary across products. We, therefore, aimed to assess real-world healthcare professional (HCP) clinical experiences in terms of usability and product performance of a gelling fiber dressing* made from highly absorbent polyvinyl alcohol fibers, as well as its silver-containing form.
Methods: Between April and July 2024, HCPs were provided with a QR code to access the survey questionnaire on a secure survey platform. Only HCPs with a minimum of 3 months’ experience of using the dressings were eligible. Survey translations were provided in several languages. HCPs were asked to answer 12 questions for each dressing: 10 focused on dressing usage in different clinical scenarios, one focused on overall dressing rating, and one asked participants if they would recommend the dressings to colleagues. At survey closure, data were extracted by a blinded statistician for analysis.
Results: 572 HCPs across >10 countries provided responses relating to the gelling fiber dressing and 243 relating to its silver-containing form. HCPs indicated their use of these products was highest for leg and foot ulcers, closely followed by pressure injuries, with additional use on surgical wounds, partial thickness burns, donor sites, and malignant wounds. 82% of HCPs indicated that the dressings are extremely effective in terms of one piece removal, 70-78% indicated that they are extremely effective at absorbing, retaining, and transferring exudate; and 70-75% indicated that they are extremely effective at facilitating patient comfort during wear. 76% of HCPs rated their overall impression of the dressings as being extremely effective.
Discussion:
The findings demonstrate the clinical utility and performance of the evaluated gelling fiber dressings in the management of chronic wounds.

.jpg)