Clinical Research
(CR-088) Customized IPC Reduction Therapy Is Shorter and More Effective in Patients with Lower Limb Lymphedema Than Classic One
Friday, May 2, 2025
7:45 PM - 8:45 PM East Coast USA Time
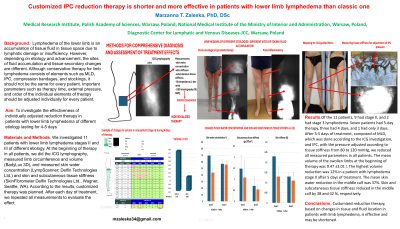
Introduction: Lymphedema of the lower limb is an accumulation of tissue fluid in tissue space due to lymphatic damage or insufficiency. However, depending on etiology and advancement, the sites of fluid accumulation and tissue secondary changes are different. Although conservative therapy for limb lymphedema consists of elements such as MLD, IPC, compression bandages, and stockings, it should not be the same for every patient. Critical parameters such as therapy time, external pressure, and order of the individual elements of therapy should be adjusted individually for every patient.
Methods: To investigate the effectiveness of individually adjusted reduction therapy in patients with lower limb lymphedema of different etiology lasting for 4-5 days.
We investigated 11 patients with lower limb lymphedema stages II and III of different etiology. At the beginning of therapy in all patients, we did the ICG lymphography, measured limb circumference and volume (BadyLux 3D), and measured skin water concentration (LympScanner; Delfin Technologies Ltd.) and skin and subcutaneous tissue stiffness (SkinFibrometer Delfin Technologies Ltd., Wagner, Seattle, WA). According to the results, customized therapy was planned. After each day of treatment, we repeated all measurements to evaluate the effect.
Results: Of the 11 patients, 9 had stage II, and 2 had stage 3 lymphedema. Seven patients had 5-day therapy, three had 4 days, and 1 had only 3 days. After 3-5 days of treatment, composed of MLD, which was done according to the ICG investigation, and IPC, with the pressure adjusted according to tissue stiffness from 80 to 120 mmHg, we reduced all measured parameters in all patients. The mean volume of the swollen limbs at the beginning of therapy was 9.47 ±3.01 l. The highest volume reduction was 12% in a patient with lymphedema stage II after 5 days of treatment. The mean skin water reduction in the middle calf was 37%. Skin and subcutaneous tissue stiffness reduced in the middle calf by 38 and 42 %, respectively.
Discussion: Customized reduction therapy, based on changes in tissue and fluid location in patients with limb lymphedema, is effective and may be shortened.
Methods: To investigate the effectiveness of individually adjusted reduction therapy in patients with lower limb lymphedema of different etiology lasting for 4-5 days.
We investigated 11 patients with lower limb lymphedema stages II and III of different etiology. At the beginning of therapy in all patients, we did the ICG lymphography, measured limb circumference and volume (BadyLux 3D), and measured skin water concentration (LympScanner; Delfin Technologies Ltd.) and skin and subcutaneous tissue stiffness (SkinFibrometer Delfin Technologies Ltd., Wagner, Seattle, WA). According to the results, customized therapy was planned. After each day of treatment, we repeated all measurements to evaluate the effect.
Results: Of the 11 patients, 9 had stage II, and 2 had stage 3 lymphedema. Seven patients had 5-day therapy, three had 4 days, and 1 had only 3 days. After 3-5 days of treatment, composed of MLD, which was done according to the ICG investigation, and IPC, with the pressure adjusted according to tissue stiffness from 80 to 120 mmHg, we reduced all measured parameters in all patients. The mean volume of the swollen limbs at the beginning of therapy was 9.47 ±3.01 l. The highest volume reduction was 12% in a patient with lymphedema stage II after 5 days of treatment. The mean skin water reduction in the middle calf was 37%. Skin and subcutaneous tissue stiffness reduced in the middle calf by 38 and 42 %, respectively.
Discussion: Customized reduction therapy, based on changes in tissue and fluid location in patients with limb lymphedema, is effective and may be shortened.

.jpg)