Clinical Research
(CR-005) Prescription Patterns Among Outpatients with Antibiotic Failure/intolerance in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI): A 2020 to 2022 Retrospective Cohort Study
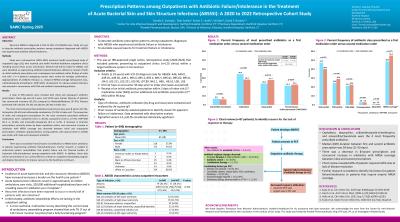
Methods: Study was a retrospective (2020–2022) electronic health record-based study of outpatients (age ≥18), who received care within Hartford Healthcare outpatient clinics including wound clinics across Connecticut. Patients had ICD-10 codes for ABSSSI, and were identified as experiencing antibiotic failure/intolerance defined as receipt of both an initial antibiotic prescription and a subsequent oral antibiotic within 90 days of initial visit with 1 in 4 patients undergoing manual chart review for etiology confirmation. Appropriateness of antibiotic therapy i.e., receipt of MRSA-coverage (tetracycline class, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (TMP-SMX), clindamycin) for abscess-related infections was assessed in concordance with IDSA and antibiotic stewardship guidance.
Results:
A total of 390 patients were included with initial and subsequent antibiotic prescriptions. Mean age was 63.3 years, and 55.9% were female. Majority of patients had commercial insurance (61.5%) compared to Medicaid/Medicare (37.4%). Patients presented with cellulitis (74.1%) and abscess (20.3%) at index visit.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotics by pharmacy class were β-lactam (47.2%), tetracycline (24.6%) and sulfonamide-combination (21.3%) at index visit. The proportion of index and subsequent prescriptions for the most commonly prescribed antibiotic medications were: cephalexin (34.4 vs 28.2%), doxycycline (23.8 vs 27.7%), TMP-SMX (21.3 vs 22.6%), and amoxicillin-clavulanate (6.9 vs 6.2%). A decrease in β-lactam prescriptions, primarily driven by fewer cephalexin orders, and concurrent increase in antibiotics with MRSA coverage was observed between initial and subsequent prescriptions. Antibiotic appropriateness among patients with abscess (64.6 vs 64.8%) was similar with index and subsequent antibiotic.
Discussion: There was an escalation from β-lactam oral antibiotics to MRSA-active antibiotics in patients experiencing antibiotic failure/intolerance. Further research is needed to understand patient comorbidities that predict failure and the financial burden of treatment failure/intolerance among outpatients with ABSSSI. In addition, these data will be instrumental in our current efforts to initiate an outpatient antibiotic stewardship program and deploy interventions to improve care across the healthcare continuum.

.jpg)