Case Series/Study
(CS-055) Use of 3% Sea Salt Cleaning Solution with Negative Pressure Wound Therapy with Instillation in a Driveline with Multi-resistant Candida Albicans
Heart Failure is defined as a syndrome caused by an anomaly in the structure and/or function of the heart, with the greatest impact on global public health, and one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality throughout the world.
Although Heart Transplantation is the most recommended treatment, mechanical circulatory assistance devices (right, left or biventricular) have emerged, which respond to the lack of donors, with the most common being the left ventricular assist device – LVAD.
The device is controlled by an extracorporeal interface, through a subcutaneous tunneled cable called driveline, which transports energy to the pump, and provides pump information to the system controller.
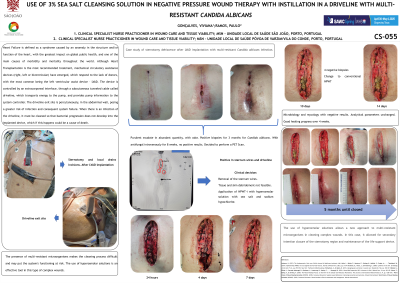
The driveline exit site is percutaneously, in the abdominal wall, posing a greater risk of infection and consequent system failure. When there is an infection of the driveline, it must be cleaned so that bacterial progression does not develop into the implanted device, which if this happens could be a cause of death. The presence of multi-resistant microorganisms makes the cleaning process difficult and may put the system's functioning at risk. The use of hyperosmolar solutions is an effective tool in this type of complex wounds.
Methods:
Case study of sternotomy dehiscence after LVAD implantation with multi-resistant Candida albicans infection.
Results:
After 8 weeks with intravenous antifungal medication, and with exudate positive for Candida albicans, the driveline is cleaned, osteosynthesis material removed from the sternum and debridement of non-viable tissue in surgery. Application of negative pressure wound therapy with instillation of a 3% sea salt cleaning solution, with hyperosmolar action in the open sternotomy and driveline insertion sites. In 4 weeks, all biopsies were negative.
Discussion:
The use of hyperosmolar solutions allows a new approach to multi-resistant microorganisms in cleaning complex wounds. In this case, it allowed for secondary intention closure of the sternotomy region and maintenance of the life support device.

.jpg)