Practice Innovations
(PI-043) Use of Kylon Fabric for Wound Hygiene and Debridement
Friday, May 2, 2025
7:45 PM - 8:45 PM East Coast USA Time
Traci Kimball, MD; Neal Lonky, MD; Frank Aviles, PT
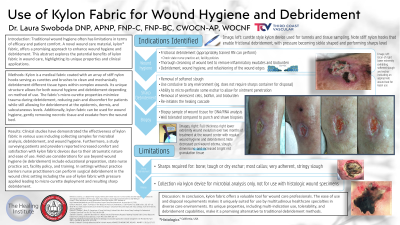
Introduction: Traditional wound hygiene often has limitations in terms of efficacy and patient comfort. A novel wound care material, kylon fabric, offers a promising approach to enhance wound hygiene and debridement. This abstract explores the potential benefits of kylon fabric in wound care, highlighting its unique properties and clinical applications.
Methods: Kylon is a medical fabric coated with an array of stiff nylon hooks serving as curettes and brushes to clean and mechanically debridement different tissue types within complex wounds. Its unique structure allows for both wound hygiene and debridement depending on method of use. The fabric's micro-curette properties minimize trauma during debridement, reducing pain and discomfort for patients while still allowing for debridement at the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous levels. Additionally, kylon fabric can be used for wound hygiene, gently removing necrotic tissue and exudate from the wound bed.
Results: Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of kylon fabric in various uses including collecting samples for microbial analysis, debridement, and wound hygiene. Furthermore, a study surveying patients and providers reported increased comfort and satisfaction with kylon fabric devices due to their atraumatic nature and ease of use. Field use considerations for use beyond wound hygiene (ie debridement) include educational preparation, state nurse practice act, facility policy, and training. In settings without practice barriers nurse practitioners can perform surgical debridement in the wound clinic setting including the use of kylon fabric with pressure applied leading to micro-curette deployment and resulting sharp debridement.
Discussion: In conclusion, kylon fabric offers a valuable tool for wound care professionals. The ease of use and disposal requirements makes it uniquely suited for use by multitudinous healthcare specialties in diverse care environments and. Its unique properties, including multi-indication use, tolerability, and debridement capabilities, make it a promising alternative to traditional debridement methods.
Methods: Kylon is a medical fabric coated with an array of stiff nylon hooks serving as curettes and brushes to clean and mechanically debridement different tissue types within complex wounds. Its unique structure allows for both wound hygiene and debridement depending on method of use. The fabric's micro-curette properties minimize trauma during debridement, reducing pain and discomfort for patients while still allowing for debridement at the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous levels. Additionally, kylon fabric can be used for wound hygiene, gently removing necrotic tissue and exudate from the wound bed.
Results: Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of kylon fabric in various uses including collecting samples for microbial analysis, debridement, and wound hygiene. Furthermore, a study surveying patients and providers reported increased comfort and satisfaction with kylon fabric devices due to their atraumatic nature and ease of use. Field use considerations for use beyond wound hygiene (ie debridement) include educational preparation, state nurse practice act, facility policy, and training. In settings without practice barriers nurse practitioners can perform surgical debridement in the wound clinic setting including the use of kylon fabric with pressure applied leading to micro-curette deployment and resulting sharp debridement.
Discussion: In conclusion, kylon fabric offers a valuable tool for wound care professionals. The ease of use and disposal requirements makes it uniquely suited for use by multitudinous healthcare specialties in diverse care environments and. Its unique properties, including multi-indication use, tolerability, and debridement capabilities, make it a promising alternative to traditional debridement methods.

.jpg)