Evidence-Based Practice
(EBP-009 (RPT-002)) Reducing Endotracheal Tube Securement Medical Device-related Pressure Injuries in Critical Care Through Multidisciplinary Approach
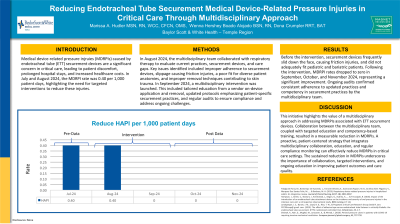
Medical device-related pressure injuries (MDRPIs) caused by endotracheal tube (ETT) securement devices are a significant concern in critical care, leading to patient discomfort, prolonged hospital stays, and increased healthcare costs. In July and August 2024, the MDRPI rate was 0.40% per 1,000 patient days, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to reduce these injuries.
Methods: Multidisciplinary team collaborated with respiratory therapy in August 2024 to evaluate current practices, securement devices, and care gaps. Key issues identified included improper adherence of securement devices, slippage causing friction injuries, poor fit for diverse patient anatomies, and improper removal techniques contributing to skin trauma. In September 2024, a multidisciplinary intervention was launched. This included tailored education from vendor on device application and removal, updated protocols emphasizing patient-specific securement practices, and regular audits to ensure compliance and address ongoing challenges.
Results: Before the intervention, securement devices frequently slid down the face, causing friction injuries, and did not adequately fit pediatric or bariatric patients. Following the intervention, MDRPI rates dropped to zero in September, October, and November 2024, representing a significant improvement. Ongoing audits confirmed consistent adherence to updated practices and competency in securement practices by the multidisciplinary team.
Discussion: This initiative highlights the value of a multidisciplinary approach in addressing MDRPIs associated with ETT securement devices. Collaboration between the multidisciplinary team, coupled with targeted education and competency-based training, resulted in a measurable reduction in MDRPIs.
A proactive, patient-centered strategy that integrates multidisciplinary collaboration, education, and regular compliance monitoring can effectively reduce MDRPIs in critical care settings. The sustained reduction in MDRPIs underscores the importance of collaboration, targeted interventions, and ongoing education in improving patient outcomes and care quality.

.jpg)

