Case Series/Study
(CS-108) Application of Air-dried Human Amniotic Membrane* on Nonhealing Diabetic Foot Ulcer for a Diabetic Patient with Chronic Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Spinal Stenosis
Friday, May 2, 2025
7:45 PM - 8:45 PM East Coast USA Time
Connie Chung, PhD – Director of Product Development, C5 Biomedical; Samera Taki, BS – Clinical Research Coordinator, Mobile Doctor Medical Clinic
Introduction: Air-dried human amniotic membrane (dHAM) is a sterile placental allograft derived from amniotic membrane tissue developed for wound healing applications. This clinical case study evaluates treatment outcomes for a patient with a nonhealing diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) managed with dHAM plus standard of care (SOC). Patient is a 100-year-old, non-smoking female with a BMI of 18-19 and PMH of diabetes mellitus type 2, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and spinal stenosis. Need for expedited healing arose as the wound persisted and risk of osteomyelitis and/or amputation increased.
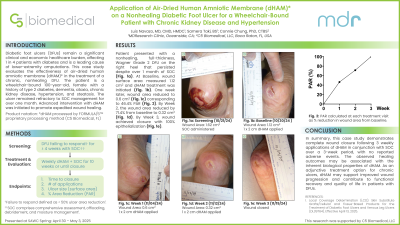
Methods: Patient presented with a nonhealing, full thickness, Wagner 2 DFU on the right heel that persisted despite over one month of SOC. At baseline visit, wound surface area was 1.12 cm2. Patient received dHAM plus SOC (including compression, debridement, offloading, moisture management) weekly for three weeks. Evaluation of wound healing was determined by time to closure, number of applications, and percent area reduction from baseline (PAR).
Results: By the third and final dHAM application, in conjunction with SOC, the wound surface area measured 0.32cm2, reflecting 71.4% PAR. Wound closed one week later. In sum, three applications of dHAM over three weeks plus SOC augmented complete wound closure without adverse events.
Discussion: This case study highlights the safety and efficacy of dHAM treatment in treating a nonhealing DFU that failed to heal with SOC alone for over one month. The biological properties of dHAM likely played a crucial role in achieving positive healing results. Therefore, dHAM is a noteworthy treatment option for chronic ulcers to promote faster healing, improved quality of life, and functional recovery.
Methods: Patient presented with a nonhealing, full thickness, Wagner 2 DFU on the right heel that persisted despite over one month of SOC. At baseline visit, wound surface area was 1.12 cm2. Patient received dHAM plus SOC (including compression, debridement, offloading, moisture management) weekly for three weeks. Evaluation of wound healing was determined by time to closure, number of applications, and percent area reduction from baseline (PAR).
Results: By the third and final dHAM application, in conjunction with SOC, the wound surface area measured 0.32cm2, reflecting 71.4% PAR. Wound closed one week later. In sum, three applications of dHAM over three weeks plus SOC augmented complete wound closure without adverse events.
Discussion: This case study highlights the safety and efficacy of dHAM treatment in treating a nonhealing DFU that failed to heal with SOC alone for over one month. The biological properties of dHAM likely played a crucial role in achieving positive healing results. Therefore, dHAM is a noteworthy treatment option for chronic ulcers to promote faster healing, improved quality of life, and functional recovery.

.jpg)